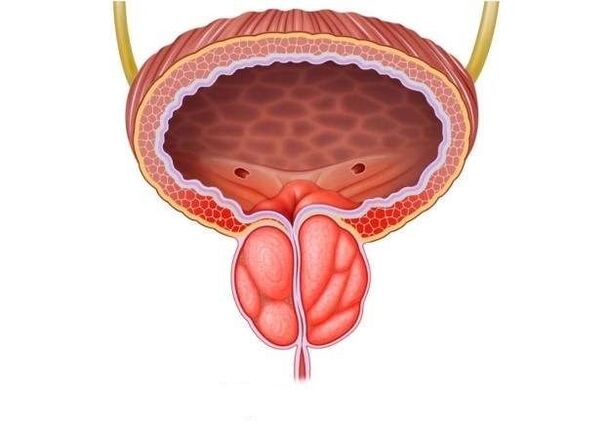
Prostate inflammation today is the leader in the group of male diseases that are mostly sexually transmitted. Its complications threaten infertility, decreased libido, and impotence.
Symptoms of prostatitis are not only pain, urinary disturbances, and inflammation of the spermatic cord. The most dangerous consequence of advanced inflammation can be the degeneration of prostate gland cancer. While pathological processes that are diagnosed on time are easy to stop.
Causes of inflammation
The risk of developing prostate inflammation increases due to various factors that predispose to the disease:
- Hypothermia, one-time or associated with the nature of work in the open air.
- A sedentary lifestyle leads to digestive system dysfunction.
- Chronic somatic diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypertension).
- Focal, perifocal focus of infection (rhinitis, tonsillitis, stomatitis, gastritis).
- Continuous UGI (chlamydia, trichomoniasis, herpes virus).
- Stress, insomnia, chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Decreased immunity due to illness, surgery, emotional stress.
- Bad habits that lead to the development of intoxication: alcohol, smoking, strong coffee.
- Occupational injuries to the perineum of car drivers, athletes, workers in dangerous industries.
- Promiscuous sex life, disturbed sexual intercourse, lack of sensual intercourse with incomplete ejaculation, prolonged absence of intimacy (low need for sperm leads to stagnation in the gland).
- Venereal disease.
Despite a large number of provocative moments, the essence of prostatitis is the occurrence of stagnation in the organ against the background of impaired blood circulation and lymph outflow.
Symptoms of prostatitis
Prostatitis can be suspected based on the following disturbances in the function of the genitourinary system:
- discomfort during urination, uncontrollable urination;
- potency disorder, weak erection, decreased libido;
- difficulty urinating, a sense of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- pain in the perineum when sitting for a long time, for example while driving;
- infertility.
The acute stage of the disease causes significant discomfort. This phase is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- painful urge to urinate;
- delay or inability to urinate;
- throbbing pain in the perineum, which is transmitted to the anus and increases during defecation. As a result, difficulty defecating;
- general intoxication, fever.
The chronic form of prostatitis is accompanied by other symptoms:
- slight increase in body temperature;
- constant fatigue;
- mild pain in the perineum, burning in the urethra;
- discomfort during urination and defecation;
- sexual function weakness and resulting psycho-emotional depression.
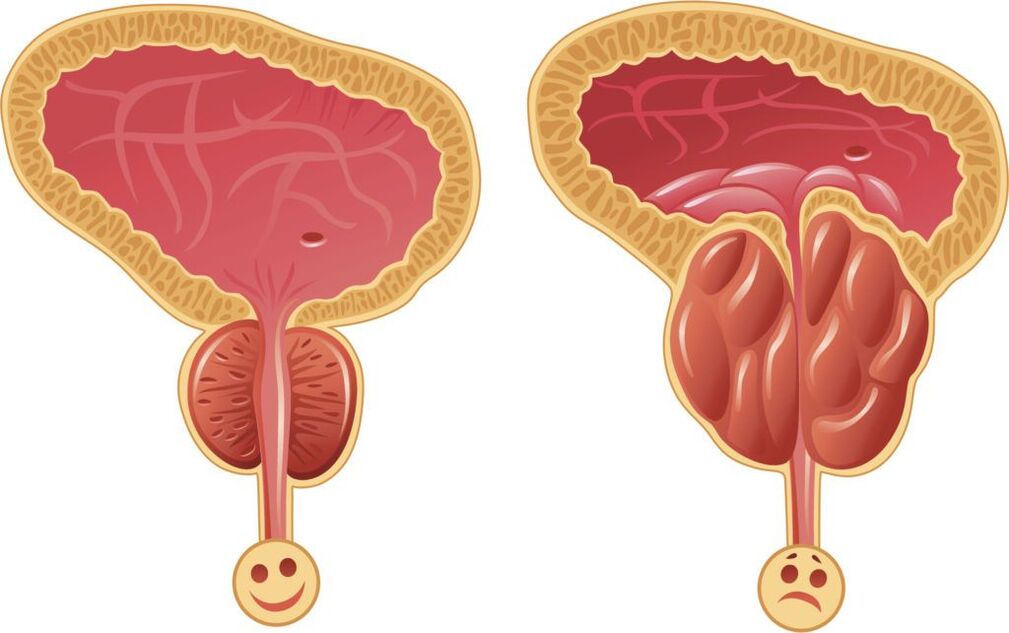
Classification
In modern urology there is no uniform classification of this disease. However, practicing doctors prefer this option to classify the inflammatory process in the prostate
According to the course of the disease:
- Acute prostatitis. It accounts for more than 50% of disease cases in people no older than 30-35 years.
- Chronic choice. It is considered a non-age category. It does not show itself for a long time; the impetus for its development is a cold or infection.
For reasons that cause pathology:
- Bacterial inflammation of the prostate gland, predominates in men under the age of 40, occurs on the background of ultrasonography, and does not go beyond the boundaries of the organ.
- Non-bacterial pathological changes in the glands, mostly chronic.
- Viral inflammation of the prostate is characterized by an acute course that affects the entire genital area.
According to the nature of structural changes in the prostate gland:
- Fibrous prostatitis is characterized by rapid growth of the gland that is irreversible and requires radical intervention. Clinically resembles prostate adenoma.
- Calculus inflammation of the prostate gland occurs due to the formation of stones in the prostate. Considered a sign of cancer.
- Congestive prostatitis, the result of an inactive lifestyle, is diagnosed in every second patient.
Signs of illness
If a man finds at least two of the following symptoms of prostatitis, he should immediately contact a qualified specialist:
- Urinary disturbances with intermittent, weak, unusually short flow of urine, causing splashing, difficulty and pain before urinating. Frequent urges to empty the bladder occur especially at night.
- Pain, located in the lower abdomen, radiates to the scrotum, perineum, and rectum.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Ejaculation problems, changes in sperm (consistency, quantity).
Acute prostatitis
The disease begins with a sudden increase in temperature (up to 40 degrees), painful headache, and fever. The symptoms that appear are accompanied by pain in the groin, perineum, back, coming out of the urethra, frequent urination and a constant desire to urinate.
Emptying the bladder occurs with delay and a burning sensation. The urine itself becomes cloudy and may contain blood. Irritability and fatigue occur.
The result of acute prostatitis can be a complete resolution of the process (if treatment is started on time). Since changes occur in many pelvic organs, they cannot be left to chance, otherwise the corresponding complications will arise:
- Vesiculitis is an inflammation of the seminal vesicles, the cause of the appearance of pus in the sperm, which not only reduces the quality of ejaculation, but leads to the loss of reproductive function.
- Colliculitis - inflammatory changes in the seminal tubercles become the reason for the development of severe pain during intercourse, orgasm disorders, and impotence of a psychological nature.
- The formation of an abscess in the body of the prostate, its rupture, and purulent damage to the rectum lead to worsening symptoms, severe intoxication, and even death.
- Stagnation in prostate tissue leads to changes in their structure, disruption of conservation, blood supply, both to the gland itself and to nearby organs, with disruption of their function. Erection becomes insufficient for full sexual intercourse, premature ejaculation and prolonged sexual intercourse without orgasm is observed.
- Cicatricial changes in the spermatic glands and cord lead to infertility, decreased sperm quality, and sperm motility. Narrowing of the urethra interferes with the normal process of urination; Bladder obstruction can cause acute urinary retention, requiring emergency surgical care.
Chronic prostatitis
The main feature of this disease is the vagueness of clinical symptoms with a long and continuous process. More often, the chronic form occurs independently, as the main pathology against the background of blood stagnation in the ducts (prostatosis), abacterial prostatitis.
The main symptoms of chronic prostatitis are:
- fever;
- pain occurs in the scrotum, perineum, anus, back;
- urinary disorders;
- mucus or mucopurulent discharge from the rectum, urethra, even without urination or defecation;
- erectile dysfunction, painful ejaculation, disturbed sexual intercourse, prolonged sexual intercourse without satisfaction.
Inaction and improper treatment of chronic prostatitis can cause complications:
- Infertility is the result of chronic inflammation in the spermatic cord, vesicles, testicles, and appendages.
- Cystitis, pyelonephritis (other diseases of the genitourinary system) are the result of hematogenous and mechanical spread of microbes.
- Sepsis.
- Continued decline in immunity.
- Untreated prostatitis can lead to cancer in 35-40% of cases.
Diagnostics
The clinical picture of this disease is typical, so the diagnosis is not difficult. It is performed by a urologist based on the medical history, patient examination, minimal laboratory use of the most modern medical devices:
- Rectal examination of the gland, taking secretions for examination (culture with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics).
- UAC, UAM, urine bacterial culture.
- Smear test for STD, UGI examination.
- Daily monitoring of urinary rhythm, measurement of urinary rate (uroflowmetry).
- For differential diagnosis, ultrasound or TRUS is performed.
- If necessary to exclude oncology, a biopsy is taken, urography is performed, and PSA is determined - prostate-specific antigen.
- To diagnose infertility, a spermogram is prescribed - an analysis of ejaculate to determine a man's fertility.
Based on the results of the examination of the patient, an individual scheme for the complex treatment of prostatitis is prepared. When prescribing the drug, the pathological form and the presence of concomitant diseases are taken into account. The decision about where to carry out therapy (inpatient or outpatient) is made by the doctor. The course of treatment is carried out with careful laboratory monitoring of the results.

Treatment of acute prostatitis
Acute prostatitis requires bed rest, a special salt-free diet, and sexual rest.
Course treatment method:
- The most effective treatment for prostatitis is etiotropic therapy. If the basis of prostatitis is an infection, a course of antimicrobial agents is a priority, which relieves the manifestations of inflammation.
- Pain syndrome is eliminated with analgesics, antispasmodics, rectal suppositories, microenemas with warm solutions of painkillers. NSAIDs can be used.
- Immunostimulants, immunomodulators, enzymes, vitamin complexes, and combinations of microelements have proven their effectiveness.
- Physiotherapy methods are only possible in the subacute stage of the disease. They improve microcirculation and improve immunity: UHF, microwaves, electrophoresis, laser, magnetic therapy.
- Massage is another effective method to influence the prostate. It opens the channels, normalizes blood circulation in the scrotum and pelvis.
- Acute renal filtrate retention can be corrected by catheterization and trocar cystostomy.
- The purulent process involves surgical intervention.
- Psychologist consultation.
Therapy for acute inflammation of the prostate is complex.
Effective treatment of acute prostatitis in men includes drugs from different pharmacological groups:
- Antibiotics.Drugs with a broad spectrum of activity are used, which have a bactericidal effect on most pathogens. Often, antimicrobial treatment is an etiotropic measure, because in most cases the cause of prostate inflammation is a microbial pathogen. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed, for viral infections, antiviral drugs are prescribed, and if protozoa are detected, anti-trichomonas drugs are prescribed. The selection of antimicrobial agents is carried out empirically or based on the results of PCR, bacterioscopy, and bacterial culture. The selection of antimicrobial agents, determination of their dosage, frequency and duration of administration can be done exclusively by the attending physician. Together with antibiotics, uroseptics can be prescribed, which have a disinfecting effect on the mucous membrane of the genitourinary tract.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.Allows you to reduce the severity of tissue swelling and pain intensity. As a rule, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used for this.
- Vascular medicine– reduces tissue swelling, relieves congestion in the prostate, thereby helping to reduce pain, improve blood circulation and local metabolic processes in the tissue.
- Enzymes– thins prostate secretions and promotes drainage of pus. In addition, enzymatic drugs increase the effectiveness of antimicrobial treatment by increasing the absorption of its active substances by the affected tissues.
- Diuretic (diuretic).They increase the production of urine, which contributes to the mechanical "washing" of the infection.
- While taking antibiotics, patients are prescribed hepatoprotectors that protect the liver parenchyma from toxic damage and improve its functional state.
- To eliminate and prevent the development of intestinal dysbiosis during antibiotic therapy, patients are prescribed probiotics.
- After the phenomenon of acute inflammation in the prostate gland subsides, the patient is prescribed a course of physiotherapeutic treatment - medical electrophoresis, galvanization, magnet, laser, mud therapy, etc. Such procedures improve local microcirculation and lymphatic drainage, metabolic processes and tissue nutrition, stimulate tissue repair, accelerate the final resolution of the inflammatory process, promote tissue recovery and normalization of the functional state of the prostate.
General activities must be carried out.
A diet for acute prostatitis in men is indicated, including a sufficient supply of easily digestible proteins and vitamins.
During the period of inflammatory swelling, spicy, fried, fatty, salty, and pickled foods are excluded from the diet.
Alcohol consumption is excluded, smoking cessation, abstinence from sexual intercourse and intense physical activity, including sports, are recommended.
It is necessary to normalize sleep, work and rest, and balance the emotional background.
During the period of illness, a person needs functional rest.
With timely, correct diagnosis and treatment of acute prostatitis in a medical institution, the prognosis is good - complete recovery occurs.
If acute prostatitis develops, seek medical advice immediately and do not self-medicate.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
With long-term effects, the course (at least a month) on the prostate, there is no 100% guarantee of recovery. Priority is given to herbal medicines, immunocorrection, changing household habits:
- Herbal preparations are widely used in urological practice. They can accumulate at the site of the most active pathological processes, protect cells from oxidation, eliminate free radicals, and prevent the proliferation of glandular tissue.
- Antibacterial therapy is selected individually, based on the sensitivity of the microbe to the drug.
- Drugs that improve immunity not only help to overcome prostatitis, they also correct the negative effects of antibiotics that interfere with the functioning of the immune system.
- The pain syndrome is relieved by giving alpha blockers and muscle relaxants.
- Prostate massage allows you to mechanically remove the "extra" secretions of the gland through the urethra, improve blood circulation, and minimize congestion.
- Physiotherapy: laser, magnet, ultrasound, iontophoresis, warm sitz bath or microenemas with herbs.
- In severe cases, intravenous fluids with diuretics are indicated. This stimulates the production of copious amounts of urine, preventing hangover symptoms, the development of ascending cystitis, and pyelonephritis.
- For constipation, herbal laxatives are used.
- Urologists and psychologists, together with the patient, develop an individual long-term program of daily routine, necessary rest, diet, dosed physical activity, and sexual activity.
- If the chronic process is resistant to therapy and the outflow of urine is blocked, surgical intervention is prescribed: removal of all affected tissue (transurethral removal of the prostate) or complete removal of the gland with surrounding tissue (prostatectomy). Practiced in exceptional cases, it is fraught with impotence and urinary incontinence. Young people do not undergo surgery because it can cause infertility.
Treatment with drugs
Treatment of prostatitis through antibacterial therapy must begin with a bacterial culture, the purpose of which is to assess the body's sensitivity to this type of antibiotic. If urination is disturbed, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs gives good results.
The medicine is taken in tablets, in acute cases - as a dropper or intramuscularly. Rectal suppositories are effective for treating chronic forms of prostatitis: with their help, drugs reach their goals faster and have minimal effects on other organs.
Blood thinning and anti-inflammatory drugs have also proven effective.
Antibacterial therapy
Antibiotics are effective drugs in the fight against bacterial prostatitis. To achieve the desired effect and not harm the body, the choice of medicine, dosage and treatment regimen should be made by a doctor. In order to correctly choose the most effective drug, he needs to know the type of pathogen that causes prostatitis, and also test the patient for tolerance to a certain group of antibiotics.
Antibiotics from the fluoroquinolone group have proven themselves effective in the treatment of chronic prostatitis. Their actions are aimed at blocking bacterial infections and strengthening the body's own immunity. In addition, the bacteriostatic antibiotic trimethoprim is recommended for the prevention and treatment of concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system.
Treatment of prostatitis caused by mycoplasma and chlamydia can also be done with drugs from the macrolide and tetracycline groups, which slow down the spread of the infection.
The duration of taking antibacterial drugs is from 2 to 4 weeks. In case of positive dynamics, the course can be extended.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy techniques in the treatment of prostatitis aim to activate blood circulation in the pelvic area, improve metabolic processes in the prostate gland, and clean the ducts. If physiotherapy is combined with taking antibiotics, the effect of the latter is enhanced.
The main methods include:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- warm up;
- ultrasound;
- mud therapy;
- high frequency irradiation;
- physiotherapy.
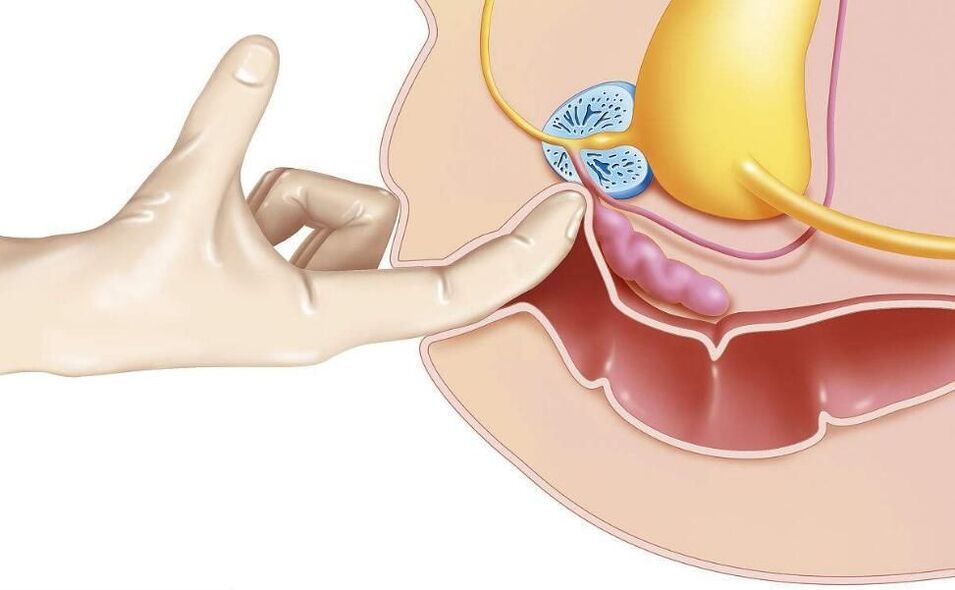
One of the oldest methods, transrectal massage of the prostate gland, according to modern research, has no proven effectiveness.
Treatment is not specific
Non-specific methods of treating prostatitis include:
- hirudotherapy;
- therapeutic fasting;
- acupuncture;
- diet according to the Ostrovsky method;
- body alkalinization using the Neumyvakin method.
We strongly recommend that you discuss all non-traditional methods of treating prostatitis with your doctor.
Surgery
Surgical methods are used in complex and emergency cases:
- for purulent abscess drainage, which is removed by laparoscopic method through puncture;
- in case of difficulty urinating due to damage to the urinary tract;
- with a large amount of affected area;
- with a large number of stones in the body of the gland.
Stones and sclerotic tissue are removed using endoscopic methods. In the case of a large affected area or many stones, resection of the prostate should be performed.
Transurethral resection is also effective for bacterial prostatitis. In this way, the risk of relapse can be reduced.
People's recovery

Treatment of prostatitis with folk remedies is unlikely to be effective by itself, but in combination with drugs and physiotherapeutic methods it may be possible to use. These include: beekeeping products, decoction of herbs and seeds, garlic tincture, ginger, beaver flow, fresh vegetables, pumpkin seeds.
In acute cases of this disease, you must consult a doctor, and you cannot self-medicate! If the purulent abscess bursts, death is possible.
Suppositories for prostatitis
Treatment of prostatitis with rectal suppositories is much more effective than tablets, if only because the rectum is closer to the prostate, which means the medicine will act faster.
The composition of drugs for the treatment of prostatitis can be completely different, they are prescribed to solve specific problems.
- Antibacterial agents are particularly effective for prostatitis caused by chlamydia.
- Painkillers are used for symptomatic treatment; they relieve pain well.
- Immunostimulants help improve blood circulation, relieve swelling, and are used in complex therapy.
- Herbal medicine has a mild effect. They, like wax on bee products, are used in addition to the main treatment.
- Ichthyol-based composition promotes blood flow in the intestinal mucosa, which accelerates the reduction of the inflammatory process and slightly improves immunity.
- Products based on special enzymes prevent the formation of scar tissue. It is recommended to take it as part of a complex therapy with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Side effects
For the symptomatic treatment of prostatitis in men, for example, relieving pain during urination, you can also take antispasmodics, which relax smooth muscles and thus relieve pain quickly.
General health is promoted by blood-thinning and anti-inflammatory supplements based on bee products, pumpkin oil and palm fruit extract.
Diet and lifestyle
For the treatment of prostatitis, a proper, balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle are very important. Food should not contain spicy, fried, salty or pickled foods. In acute cases, alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Food should contain enough fiber to prevent constipation. Protein content should be reduced. It is advisable to supplement the diet with herbs, ginger, and pumpkin seeds.
As a result of untreated prostatitis
Even if the symptoms of prostatitis do not appear for a long time, it is necessary to undergo a regular examination by a urologist. Prostatitis that does not heal completely may be accompanied by the formation of calcifications, which then need to be removed together with the gland. Experts are convinced that there is no other way to remove or dissolve stones.
In addition, pathogenic microorganisms can migrate to neighboring organs, causing inflammation. Advanced prostatitis can lead to the development of adenoma and prostate cancer.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of unpleasant diseases for men, you need to eliminate provoking factors and follow simple rules:
- Live a healthy lifestyle, abandon bad habits.
- Don't be too cold.
- Drink at least 1. 5-2 liters of water a day.
- Strengthen your immune system, walk more, strengthen your body.
- Engage in physical education and sports, visit fitness clubs.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Practice a normal sex life with a normal partner.